OPEN FROM 9AM TO 5PM – CLOSED ON WEEKENDS
How to Choose the Best Curing Oven for Your Specific Needs
When it comes to selecting the right curing oven for your specific needs, the decision can be daunting given the wide array of options available in the market. Industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading authority on thermal processing technologies, has noted, "A well-chosen curing oven not only enhances the quality of your products but also optimizes production efficiency." With the growing demand for high-quality cured products across various sectors, understanding the unique features and functionalities of curing ovens is essential for achieving optimal results.
Choosing the best curing oven involves considering several critical factors tailored to your operation, such as the type of materials being cured, the scale of production, and energy efficiency. An informed selection can greatly impact both the final product quality and the overall workflow of your manufacturing process. By exploring the nuances of curing ovens and leveraging expert insights, manufacturers can make educated choices that align with their specific curing requirements, ultimately leading to improved performance and satisfaction in their end products.
Understanding the Role of Curing Ovens in Manufacturing Processes
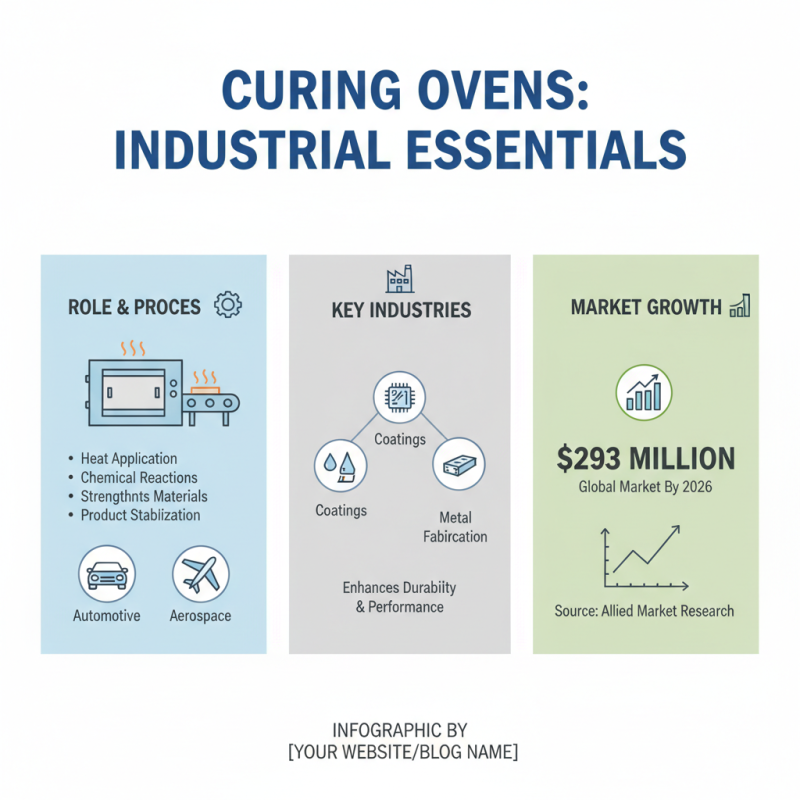
Curing ovens play a crucial role in various manufacturing processes, particularly in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and coatings. These ovens are essential for the curing of materials, which typically involves the application of heat to facilitate chemical reactions that strengthen and stabilize products. According to a report by the Allied Market Research, the global curing oven market is expected to reach $293 million by 2026, reflecting the growing importance of efficient curing technologies in enhancing product durability and performance.
The functioning of a curing oven is deeply tied to its ability to maintain precise temperature and atmospheric control, ensuring that materials are cured uniformly and efficiently. For instance, in the aerospace industry, components are often subjected to stringent quality standards, making the curing process critical for structural integrity. A well-maintained curing oven can improve production rates and reduce defects, thereby increasing operational efficiency. The use of advanced curing ovens with features like programmable controls and energy-efficient designs can lead to significant decreases in energy consumption—reportedly by up to 30%, as found in a 2022 industry study.
Furthermore, the selection of a curing oven must be aligned with specific manufacturing requirements, such as batch size and material type. For example, resins used in composite materials require consistent curing profiles to ensure optimal performance, while coatings may need varying temperatures for effective adhesion. Understanding these nuanced needs allows manufacturers to select curing ovens that not only comply with industry standards but also boost their overall productivity and product quality.
Identifying Your Specific Curing Requirements and Applications
When selecting a curing oven, the first step is to clearly identify your specific curing requirements. Different materials and applications dictate varying temperature ranges, humidity levels, and curing times. For instance, certain coatings may require low-temperature curing to maintain their integrity, while others might need high-temperature conditions to achieve optimal properties. Evaluating the thermal profile necessary for your process is crucial, as it directly influences the quality and performance of the final product.
Additionally, understanding the applications for which the curing oven will be used is vital. Whether you are working with plastics, composites, or various coatings, each will have distinct processing needs. Consideration should also be given to the production volume; larger operations may benefit from batch ovens, while smaller applications might find compact or benchtop models more suitable. By clearly articulating your specific curing needs and applications ahead of time, you can ensure that the oven you choose will efficiently meet your production goals and enhance the overall quality of your work.
How to Choose the Best Curing Oven for Your Specific Needs
| Dimension | Description | Recommended Value |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Operational temperature range for effective curing | 150°F - 500°F (65°C - 260°C) |
| Curing Time | Time required for materials to cure properly | 30 minutes - 3 hours |
| Size/Capacity | Interior space available for curing items | 3 - 10 cubic feet |
| Energy Efficiency | Rank of energy consumption relative to output | Efficient (Below 5 kWh per hour) |
| Ventilation | Necessary exhaust system for smoke and fumes | Active or passive ventilation |
| Control System | Type of controls for temperature and runtime | Digital or analog with programmable settings |
| Material Compatibility | Types of materials suitable for curing | Wood, epoxy, plastics, composites |
| Safety Features | Built-in safety functions to prevent accidents | Overheat protection, door lock, fireproof materials |
Evaluating Temperature Range and Control Features in Curing Ovens
When selecting a curing oven, one of the most critical factors to consider is its temperature range and control features. Studies indicate that a consistent temperature control is vital for achieving optimal curing results, particularly in applications like coatings and adhesives. An ideal temperature range typically falls between 100°F to 400°F (38°C to 204°C), with some specialized processes requiring even higher settings. A curing oven must maintain uniform heat distribution to avoid any discrepancies in product quality, which can lead to defects in the final output.
Moreover, advanced control features play a significant role in precision curing processes. Digital controllers with programmable settings allow users to set specific curing profiles, which can include ramp-up rates and hold times. According to a report by the American Institute of Chemical Engineers, the ability to fine-tune these parameters can enhance the efficiency of the curing process by as much as 30%. Additionally, ovens equipped with sensors and data logging capabilities enable manufacturers to continuously monitor performance and make adjustments as needed, ultimately improving productivity and product reliability. Therefore, investing in an oven with robust temperature control features not only ensures consistency but also aligns with industry best practices for quality assurance.
Comparing Different Types of Curing Ovens: Infrared, Convection, and More
When selecting a curing oven, understanding the differences between various types is crucial to meet your specific needs.
Infrared curing ovens are known for their fast heating capabilities, which make them ideal for applications requiring a quick turnaround.
The technology uses infrared radiation to heat the surface of the material directly, resulting in efficient energy use and reduced curing times.
This is especially beneficial in industries like automotive and aerospace, where time is of the essence.
In contrast, convection curing ovens circulate hot air to provide uniform heating. This type of curing is great for larger, bulkier items that need consistent temperature distribution.
Convection ovens typically take longer to reach curing temperatures compared to infrared ovens, but they are excellent for achieving thorough curing without hot or cold spots.
Understanding the attributes of these ovens can help you select the best one according to the specific materials and curing requirements you have.
Tips: Always consider the size and layout of your workspace when choosing an oven.
Ensure that you have adequate ventilation, as some curing processes can release fumes.
Additionally, investing in an oven with adjustable temperature controls and timers can enhance your curing precision, allowing you to experiment and find the perfect settings for your projects.
Budget Considerations and Maintenance Tips for Curing Ovens
When selecting the best curing oven for your specific needs, budget considerations play a significant role in ensuring you make a well-informed investment. The market for curing ovens varies widely, with prices ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on features and capabilities. According to a recent industry report, around 35% of small to medium-sized businesses in manufacturing allocate about 10-20% of their production budget toward equipment like curing ovens. Thus, determining how much you can safely invest without compromising your operational efficiency is essential.
In addition to initial costs, ongoing maintenance is vital to maximizing the longevity and performance of your curing oven. Regular maintenance checks, which according to industry standards should occur at least once every six months, can help prevent costly downtimes and repairs. A comprehensive maintenance plan can save businesses up to 25% on their operational costs by ensuring that the equipment runs efficiently and effectively. Professionals recommend keeping detailed logs of usage and service history to identify trends or potential issues early. This proactive approach not only enhances productivity but also extends the life of your curing oven, making it a sound investment for any operation.
Budget Considerations for Curing Ovens
Related Posts
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Small Paint Booth for Your Projects
-

2025 Top Digital Spray Booth Filters for Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
-

Exploring the Future of Surface Finishing with Innovative Powder Coating Equipment for Sale
-
What is Powder Coating Oven and How Does It Work for Your Projects
-

Top 7 Portable Paint Booths for Efficient Home Painting Projects
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing a Used Powder Coating Oven for Your Business

